Story
Noun
- Real people and events told for entertainment
- The commercial prospects or circumstances of a particular company

Cyber Security
In 2024, where communication heavily relies on emails, ensuring the security and authenticity of electronic messages has become more crucial than ever. In this blog post, we unravel the complexities of email security by exploring four essential components: SPF, DKIM, DNS, and DMARC. Don’t worry, we’ll keep it simple and easy to grasp!
Imagine SPF records as a VIP list for your company’s emails. Published by a company, these records contain a list of approved IP addresses allowed to send emails on behalf of the company. In simpler terms, SPF records help verify whether an email claiming to be from a specific company is legitimate or possibly a phishing attempt.
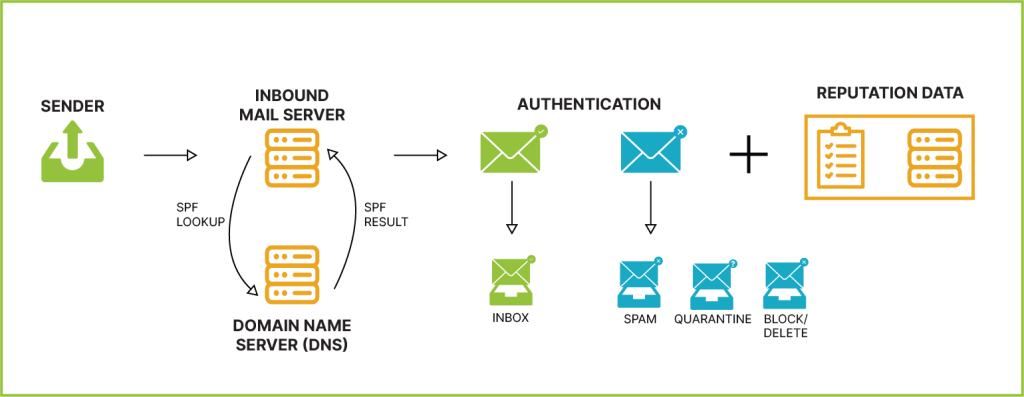
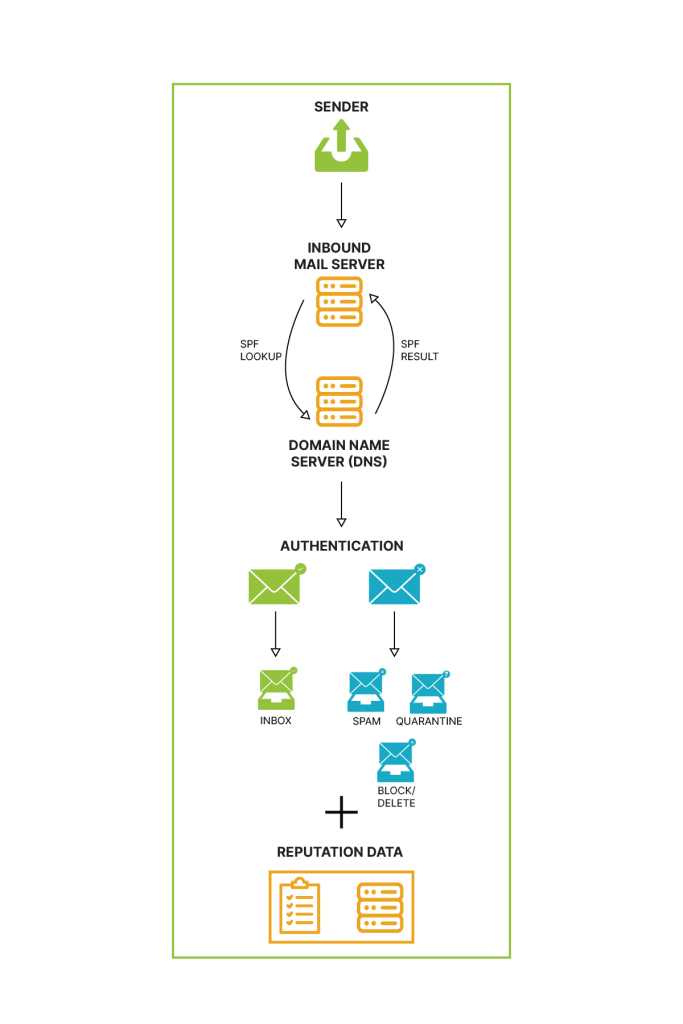
DKIM acts as a superhero against email spoofing, a deceptive technique used by cybercriminals. It’s like an invisible signature embedded in emails, working behind the scenes. This signature, not visible to the naked eye but present in the email’s code, can be authenticated using a special key stored in the DNS of the corresponding domain. When the DKIM signature matches the key, the email is validated as genuine.
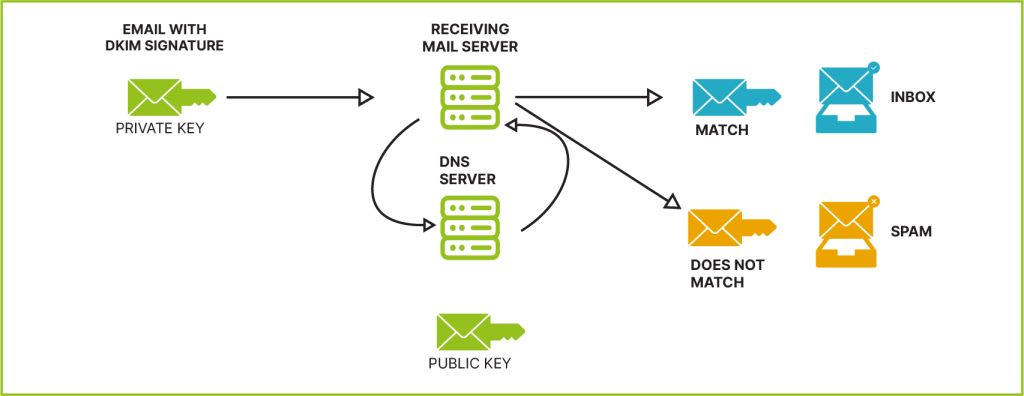
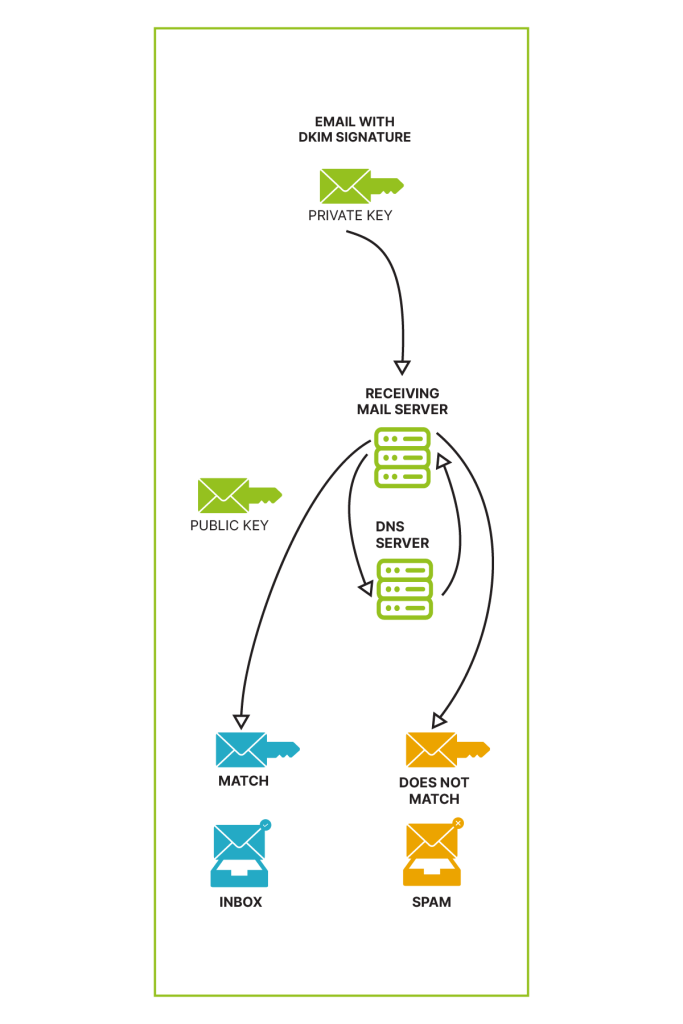
Think of DNS as the digital phone book of the internet. It contains a comprehensive listing of IP addresses and their corresponding domains. In the context of email security, DNS plays a crucial role in connecting domain names to specific IP addresses, ensuring that emails reach their intended destinations securely.
A PTR record, or pointer record, is a type of record in the Domain Name System (DNS) that maps an IP address to a domain name. This is the opposite of a standard DNS lookup, which maps a domain name to an IP address.
Think of it this way: when you type a website address into your browser, a DNS lookup happens behind the scenes to translate that address into the numerical IP address the computer needs to connect to the website. A PTR record does the opposite, taking an IP address and translating it back into a human-readable domain name.
DMARC is the email security guardian that goes above and beyond to fortify your email defenses. It conducts additional tests, including internal checks of DKIM records and SPF checks to ensure that the email’s information aligns properly. Moreover, DMARC provides detailed reports on email traffic from a specific domain, offering insights into flagged and unflagged traffic. Some services even provide a user-friendly dashboard for a clearer understanding.

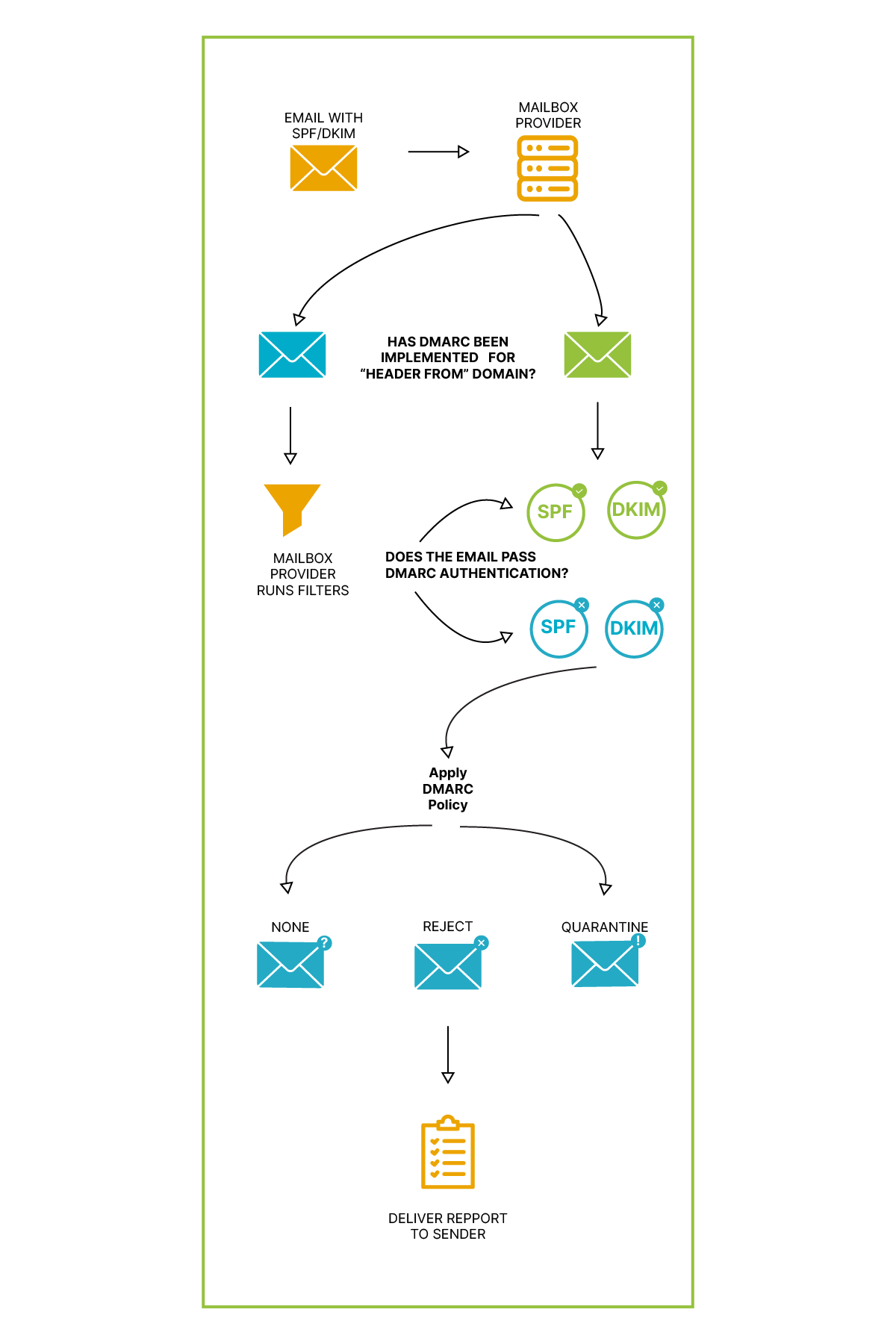
In a world where cyber threats are constantly evolving, understanding the basics of email security is crucial for individuals and businesses alike. SPF, DKIM, DNS, and DMARC work hand-in-hand to create a robust defense against phishing attempts and unauthorized access. By demystifying these terms, we hope to empower you to navigate the digital landscape with confidence and ensure the security of your email communications.
Noun
Noun